Safety
Safety
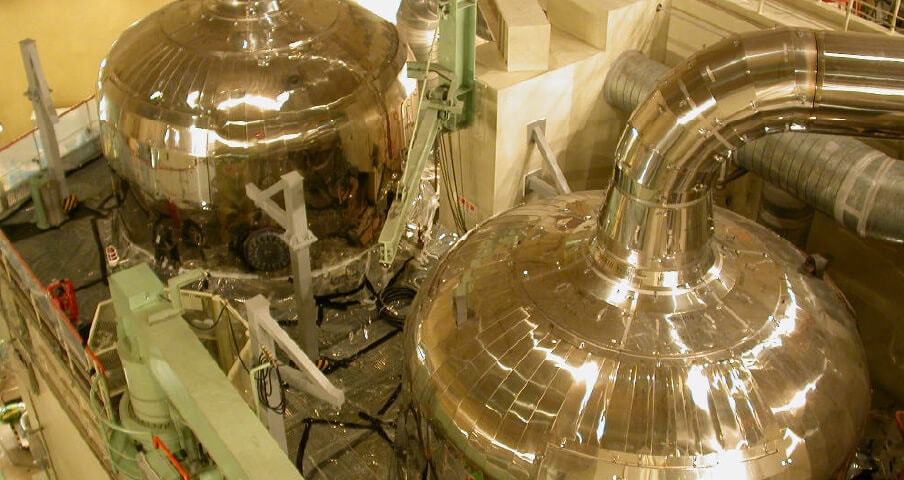
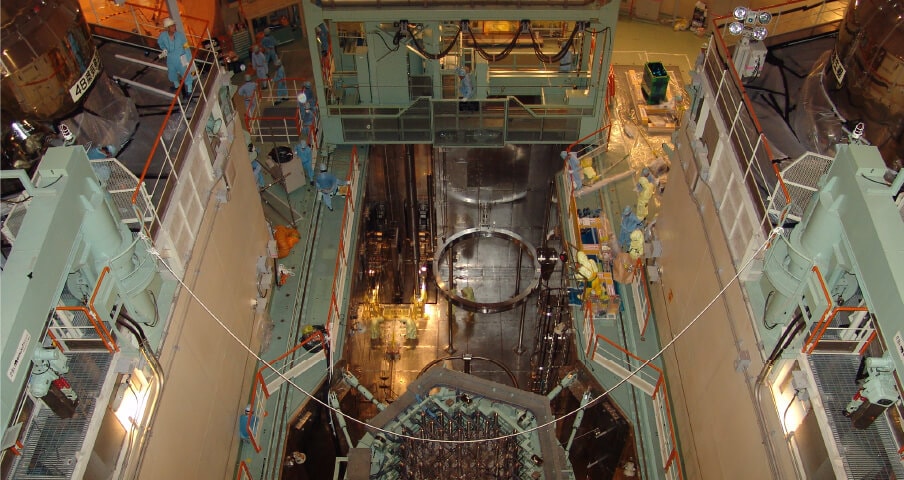
Full-scope simulator for operator training
Operators at a nuclear power plant watch over the safety of the nuclear power plant day and night. In the event of a plant failure or accident, the operator assumes an important mission of identifying the event and taking prompt action in accordance with the prescribed procedures to prevent serious incidents. In order to prepare for an emergency, we have developed a "full-scope simulator for operator training" that faithfully reproduces the equipment actually used in a nuclear power plant, by pulling our reliable nuclear expertise and advanced IT technologies together.
Using the simulator, which is equipped with calculation codes for real-time simulation, various situations are created, from small accidents to accidents that no one has ever experienced before, and the operators take action according to the situation. This way of simulator training allows operators to develop the skills needed to ensure the plant safety.In cooperation with GSE, an international simulator manufacturer in Sweden, we have developed the simulator based on the standards set by the Nuclear Standards Committee of Japan Electric Association.
The simulator is also used as a training tool for new graduates of Kansai Electric Power Company to learn about the structure of a nuclear power plant and the relationship between the behavior of the entire system and various parameters.

Safety
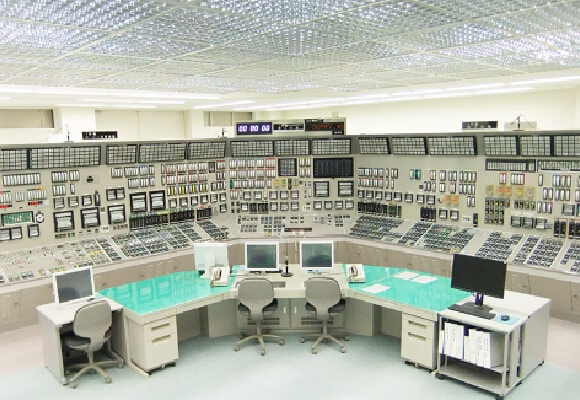
Plant Behavior Analysis (Severe Accident)
Severe Accident (SA) refers to an accident in a nuclear power plant in which the core cannot be cooled properly due to events that greatly exceed the design basis assumptions, resulting in core damage. We are analyzing thermal-hydraulic behavior, core damage and reactor vessel failure behavior, molten core and concrete reaction behavior, hydrogen release and migration behavior, and fission product (FP) release and migration behavior in the event of a severe accident at a nuclear power plant. The analysis results are utilized in the development of training data which is transmitted to the Safety Parameter Display System (SPDS) of the nuclear operator and the Emergency Response Support System (ERSS) of the national government in the nuclear emergency drills based on the Act on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness.
We also perform detailed thermal-hydraulic analysis of the plant behavior leading to the core damage.
・MAAP(severe accident analysis code)
・GOTHIC(general-purpose thermal-hydraulic behavior analysis code)
・RELAP5(transient/accident analysis code)
・COBRA-EN(subchannel analysis code)
Safety
Education and Training Support
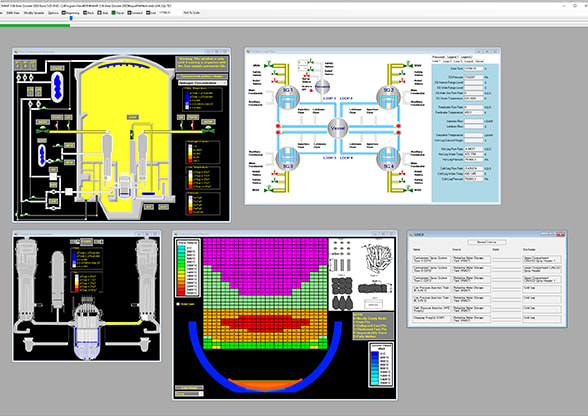
We have developed the Severe Accident Visualization Tool, a system that uses simulator calculation models to analyze and display severe accident events on a single PC, and are using the tool for severe accident training.
Features of the Severe Accident Visualization Tool
- The system represents changes in the plant condition in the event of a severe accident in visualized images, which are difficult to understand with a list of numerical numbers.
- The system also displays the behavior of internal parameters and physical and chemical changes that cannot be observed in an actual plant.
- For important points, graphs, analysis materials, and detailed plant information can be displayed from the summary screen.
For severe accident training, we use the Severe Accident Visualization Tool to explain the physical phenomena and plant behavior in the event of a severe accident, as well as the effects on the plant of activities to prevent the development and spread of an accident and to bring them under control. In addition, for personnel and leaders of the emergency response headquarters, we conduct training exercises to determine the events appropriately, take responding actions, and give instructions by displaying only trend graphs of event changes in a blind scenario.
In order to provide training based on various events, our engineers and experienced operators work in pairs to devise scenarios and create training materials based on the scenarios.
For in-house training purposes, for example, the following exercise is possible; "study the factors that affect the progression of typical events in the event of an accident, such as loss of coolant and loss of all AC power, and confirm the degree of impact by conducting sensitivity analysis”. Through the training using the Severe Accident Visualization Tool, trainees can deepen their overall understanding of plant behavior in the event of an accident at a pressurized water reactor and how to simulate the behavior.
Safety
Plant behavior analysis (assessment of radiation exposures)
We perform plant behavior analysis to evaluate the exposure doses to plant operators and the surrounding public due to radioactive materials discharged into the environment during normal operation and in the event of an accident at nuclear power plants (including decommissioned plants). The results of the assessment are mainly used to explain the assessment conditions and to calculate the exposure doses in the applications for the approval of the establishment (modification) of nuclear reactors and the approval of the construction plan (modification), which are filed by nuclear operators based on the "Law Concerning the Regulation of Nuclear Source Materials, Nuclear Fuel Materials and Reactors".
The assessment results are also used to evaluate the radiation dose from equipment containing radioactive materials inside the building to the outside of the building.
・Released radioactivity assessment
・Atmospheric dispersion assessment
・Exposure dose assessment
・QAD(Kernel Integration Code System)
・G33(Scattering Kernel Code System))
・PHITS(Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Code System)
Safety
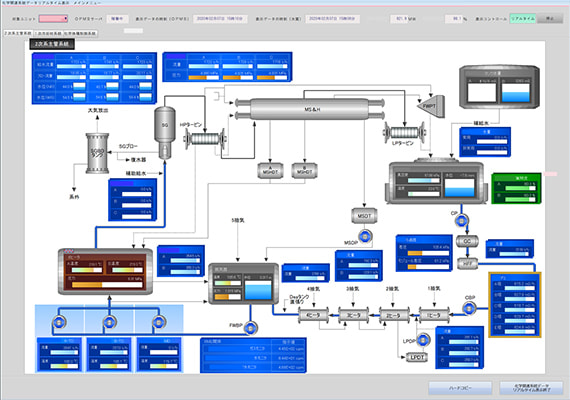
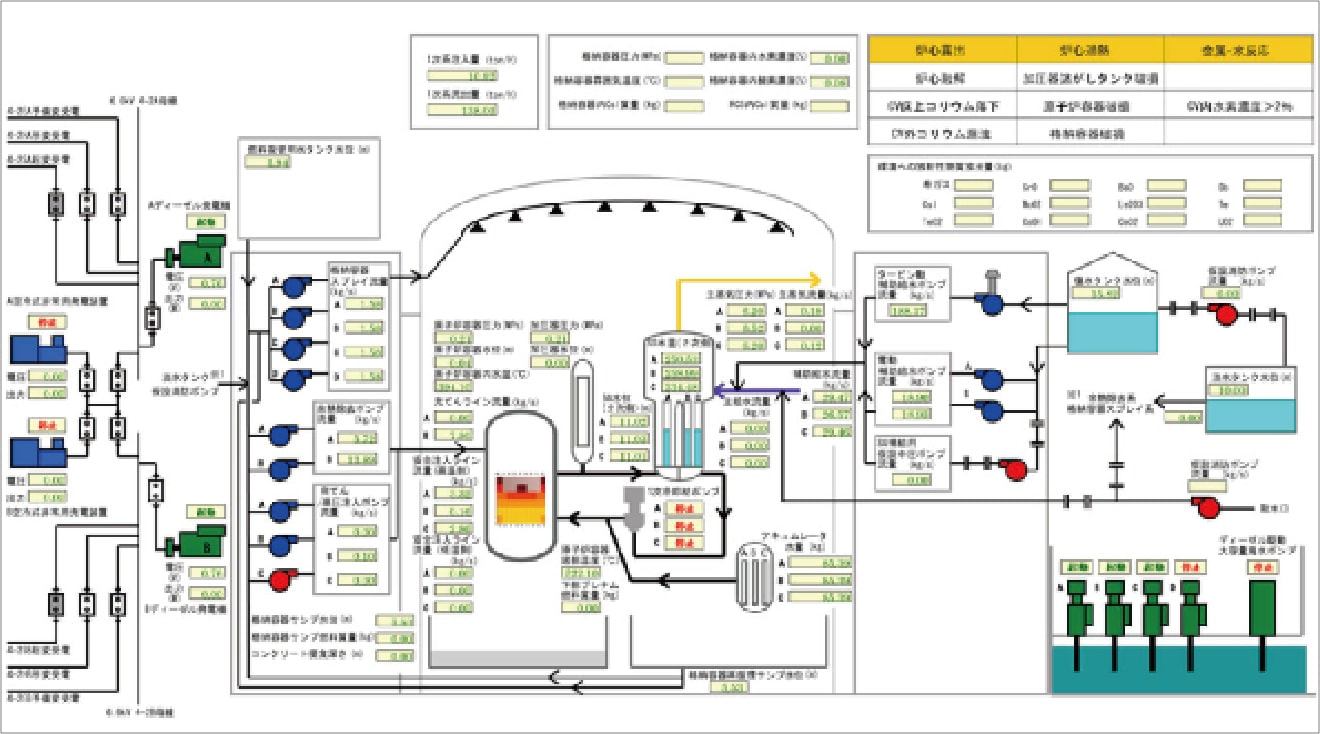
Engineering System (Operating Plant Condition Management System)
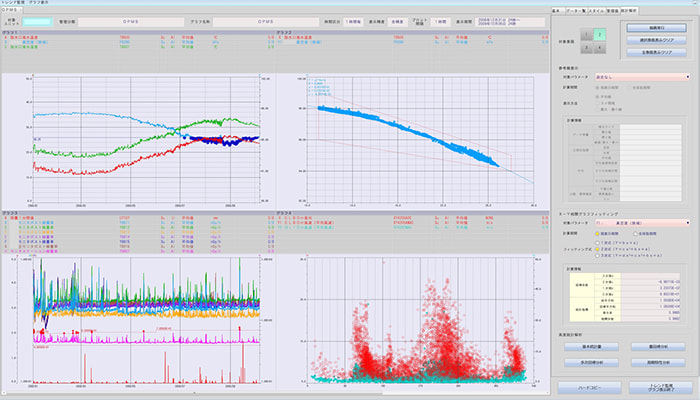
In a nuclear power plant, a vast number of sensors are installed to continuously capture every moment of plant behavior, including temperature, pressure, flow rate, water level, etc., to control the plant and ensure safety of the plant.The Operating Plant Condition Management System (OPMS) is a system that stores data obtained from these sensors and uses the data for power plant operation management.
Who protects the plants are the people working there. In order to support these people, the OPMS is in operation 24 hours a day, 365 days a year in the main control room as well as at various locations in the plant via a LAN that is spread throughout the plant to make the data obtained at thousands of data points per unit easier to view, and to evolve those data into more reliable information through statistical processing.
The OPMS has been improved together with its users under the theme of "evolving data into information". Now that we have entered the era of DX (Digital Transformation), we are facing a new challenge of how to utilize this vast amount of data assets that have been stored for a long period of time into the future.
Safety
Engineering Systems (Applications of Information Technology to Streamline Operations)
For achieving the safe operation of a nuclear power plant in compliance with the new regulatory requirements, advanced management of business operations is essential. In this respect, we are developing the systems to support a wide variety of power plant operations, including management of resident personnel in preparation for extensive disasters, training management to maintain personnel competence, and searching for domestic and overseas information about new inspection systems.
In recent years, we have also incorporated AI technologies in the field of natural language into our database to develop and provide tools that enable more advanced business operations.
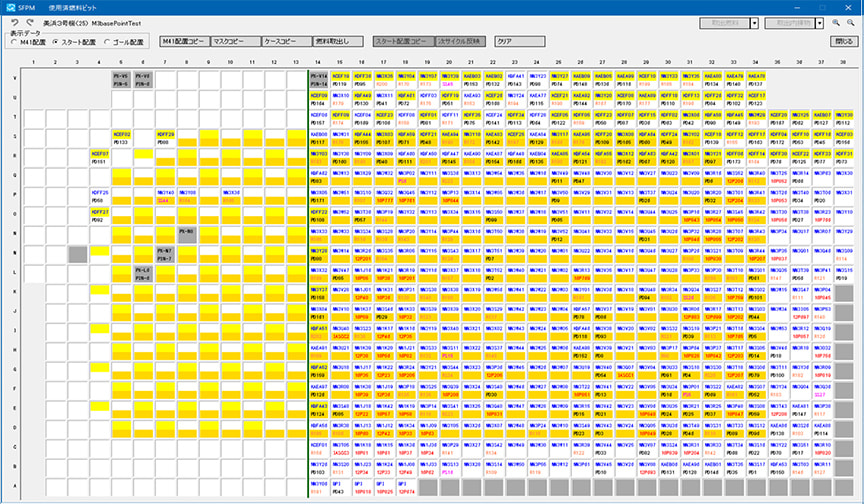
Screen of the system locating the fuel in the spent fuel pool with safety considerations